Industry Knowledge
What is plastic lighting lampshade injection molding, and how is it different from other types of injection molding?
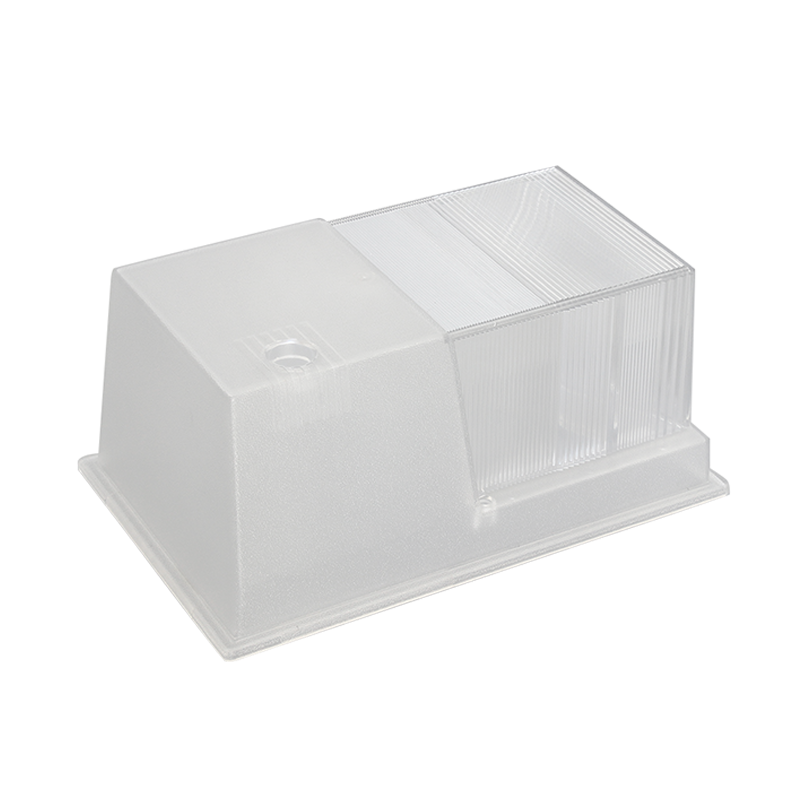
Plastic lighting lampshade injection molding is a specialized form of injection molding that is used to produce lampshades for lighting fixtures. This process involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity at high pressure and temperature. The molten plastic material then cools and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold cavity, and the finished lampshade is ejected from the mold.
Plastic lighting lampshade injection molding is different from other types of injection molding in that it requires specific design considerations and material selection to achieve the desired visual effect and light distribution. Lampshades often feature intricate designs and patterns that must be accurately reproduced in the molded part, as well as translucent or opaque surfaces that affect the way light is emitted from the lampshade.
To achieve these desired effects, the mold design and material selection must take into account factors such as light diffusion, heat resistance, and color consistency. Specialized materials, such as polycarbonate or acrylic, may be used to achieve specific visual or functional properties, such as UV resistance, fire resistance, or improved light transmission.
Overall, plastic lighting lampshade injection molding requires careful consideration of both the visual and functional aspects of the finished product, and requires specialized knowledge and expertise to achieve the desired results.
What types of plastic materials are typically used in lighting accessories injection molding, and what properties do they have?
Several types of plastic materials can be used in lighting accessories injection molding, depending on the specific requirements of the lampshade. Some common types of plastic materials used in lighting lampshade injection molding include:
1. Polycarbonate (PC): This material is a strong and durable thermoplastic that is known for its impact resistance, high clarity, and heat resistance. Polycarbonate is often used in lighting applications that require high light transmission and impact resistance, such as outdoor lighting or industrial lighting.
2. Acrylic (PMMA): Acrylic is a transparent thermoplastic that is known for its high clarity, light transmission, and scratch resistance. It is often used in lighting applications that require a smooth and glossy surface finish, such as decorative lighting or architectural lighting.
3. Polyethylene (PE): This material is a lightweight thermoplastic that is known for its flexibility and low cost. Polyethylene is often used in lighting applications that require a soft and pliable material, such as lampshade diffusers.
4. Styrene acrylonitrile (SAN): SAN is a thermoplastic that is known for its high impact resistance, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. It is often used in lighting applications that require a durable and rigid material, such as industrial lighting.
5. Polypropylene (PP): This material is a thermoplastic that is known for its high chemical resistance, low cost, and light weight. Polypropylene is often used in lighting applications that require a material that is resistant to chemicals and environmental stress, such as outdoor lighting.
Overall, the choice of plastic material for lighting lampshade injection molding will depend on the specific requirements of the lampshade, including the desired visual effect, light transmission properties, and environmental resistance.
How is the injection molding process optimized for producing high-quality plastic lighting lampshades?
The injection molding process can be optimized for producing high-quality plastic lighting lampshades through several techniques:
1. Mold design: The mold design is critical for achieving the desired lampshade shape, texture, and surface finish. The mold should be designed to minimize the potential for defects such as warpage, flash, or sink marks. The mold should also be designed to allow for easy ejection of the molded part, without damaging the lampshade.
2. Material selection: The selection of the appropriate plastic material is crucial for achieving the desired visual effect and light transmission properties of the lampshade. The material should be chosen based on factors such as clarity, color consistency, UV resistance, and heat resistance.
3. Injection molding parameters: The injection molding process parameters, such as injection speed, pressure, temperature, and cooling time, should be optimized to achieve the desired level of fill, part dimension, and surface finish. The process parameters should be carefully controlled to ensure consistent quality and minimize the risk of defects.
4. Post-molding operations: Post-molding operations, such as trimming, polishing, and assembly, can be used to improve the final visual appearance and functionality of the lampshade. These operations should be carefully controlled to minimize the risk of damage to the molded part.
5. Quality control: Quality control measures, such as visual inspection, measurement, and testing, should be used to ensure that the lampshade meets the required specifications. Any defects or deviations from the specifications should be identified and corrected promptly.
By optimizing these factors, the injection molding process can be effectively used to produce high-quality plastic lighting lampshades that meet the required functional and aesthetic requirements.

 English
English Español
Español 简体中文
简体中文