Comprehensive analysis of projects, high degree of cooperation with customers, strong timeliness, good follow-up service and stable production.
Yuyao Hualong Moulds & Plastic Products Co.,Ltd. was established in 1988. At present, there are 15 plastic injection molding machines from 100g to 3500 g, more than 20 mold manufacturing equipment such as machining centers, and more than 20 testing equipment and other auxiliary equipment. As leading Plastic Injection Molded Recognizer Shell manufacturers and Recognizer Shell factory in China, We have 100 employees and more than 30 managers and professional technicians.
After over 30 years of indomitable efforts, with the molds-making and plastic products-processing as the mainstay, our company has implemented a service for product development, mold-designing and making, plastic injection-molding and finished product-assembly in a coordinated process. Hualong mold has long history of serving European and American high-quality brands and well-known public companies at domestic and abroad. We custom make injection molded Plastic Recognizer Shell. Customized products involve all kinds of instruments, equipment accessories, industrial automation and intelligent equipment of the Internet of things, auto accessories, kitchen appliances, household products, etc. Products are widely used in power, communications, security, automotive, aerospace, medical, life and other different fields.
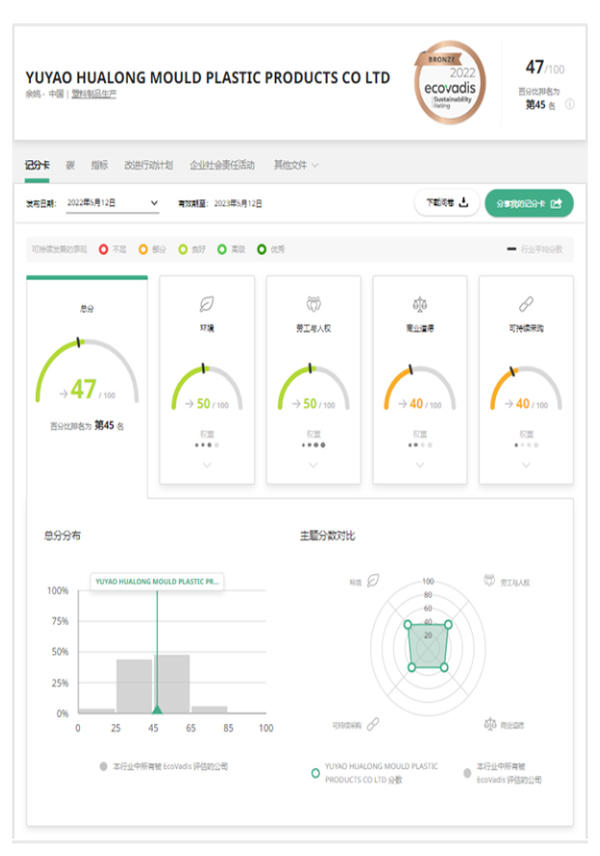
We have gained certifications of ISO9001, ISO16949 quality management system and ISO14001 environmental management system. OEM/ODM plastic injection molded Recognizer Shell. We accept annual factory inspection of clients, and conduct ECOVADIS audits on environment, labor and human rights, business ethics and sustainable procurement.

 English
English Español
Español 简体中文
简体中文